Mastering Support and Resistance: Strategies for Successful Trading
Within the world of trading, the terms Support and Resistance play pivotal roles. These critical concepts form the bedrock of technical analysis, a potent trading tool utilized by traders across the globe. This article serves as an authoritative guide to understanding, identifying, and employing support and resistance in your trading strategy.
Technical analysis is a trading discipline employed to identify trading opportunities by analyzing statistical trends gathered from trading activity, such as price movement and volume. Investopedia.
In this comprehensive piece, you will delve into:
- The essential understanding of support and resistance
- Methods for identifying support and resistance levels
- Practical techniques for integrating support and resistance into your trading strategy
- Showcasing real-world charts and graphs to illustrate these concepts
By elucidating these concepts, we aim to empower your trading prowess, helping you to make informed trading decisions grounded in an insightful understanding of the market dynamics. By the end of this article, you should see the market through a precision-focused lens.
Table of Contents
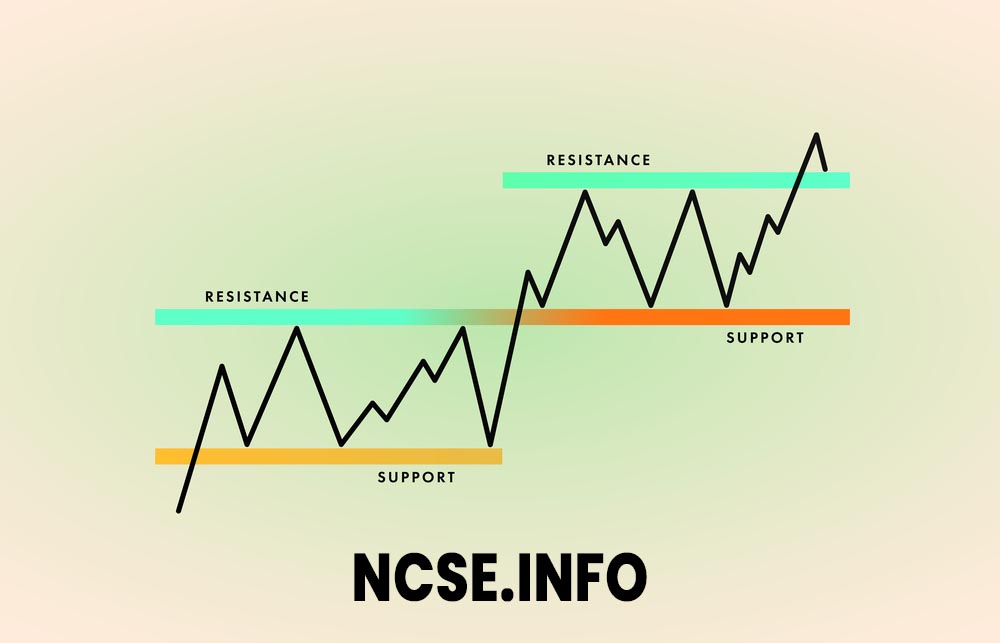
Understanding Support and Resistance in Trading
In the world of trading, two concepts play a pivotal role: support and resistance. Both phenomena are key characteristics of price action, directly shaping the market behavior and the decisions of traders. In this section, we’ll delve into the fascinating mechanics of support and resistance to arm the reader with indispensable knowledge in trading.
At its core, support in trading denotes a price level where an asset’s downward movement is halted due to the increased buying pressure. The theory relates to basic economic principles: if a product is perceived as a bargain, demand for it will escalate, stifling further price decline. Consequently, the support level genuinely reflects the point at which the market considers an asset undervalued, resulting in a surge in demand and disruption in a downward movement.
Resistance, on the other hand, represents a specific price level that an asset finds difficult to breakthrough due to increased selling pressure. As an asset’s price ascends towards the resistance level, market participants begin seeing it as overpriced. Thus, supply spikes as more investors sell, and this selling pressure stifles further elevation in price, forming a resistance level. In essence, resistance embodies the price level where the market believes an asset to be overvalued and, thus, triggers an increase in supply, stymieing an upward run.
Identifying and understanding these two key levels – support and resistance – lays the foundations for technical analysis in trading. These levels provide traders with information on the price points at which an asset becomes a potential buy or sell. However, these levels are not typically static, often flexing with market sentiment and economic data.
Both support and resistance levels contribute to the construction of trend lines and channels, each of which is a valuable tool in forecasting market trends. The interplay between these concepts provides a cogent framework for anticipatory trading strategies, and as such, they play an indispensable role in any trader’s analytical toolkit.
In the following sections, we’ll explore more in-depth how to identify and strategize around these critical trading levels. Begin to develop a keen eye for these key points, and you’ll enhance your proficiency and competitiveness as a trader.
Identifying Support Levels in Trading
In the realm of trading, identifying support levels is vital for successful execution of strategies and overall profitability. A support level refers to the price point at which a stock, currency, or commodity is anticipated to stop falling and potentially begin to rise. It’s primarily driven by the law of demand and, hence, the idea of buying ‘low’ to later sell ‘high’ is centered around these crucial levels.
To identify a support level, one needs to study the historical market data of a particular security or commodity and assess the trend lines. These trend lines are graphical representations of the stock price over time, which help traders identify patterns and predict future movements.
A support level in a price chart typically exhibits the following characteristics:
- Repeated bottoms: If the price of a security frequently falls to a certain level and then starts increasing, this level can be considered as a potential support.
- Bouncing: At the support level, prices tend to ‘bounce’ up, indicating that buyers are stepping in and willing to purchase at this price.
- Increased trading volume: An increased level of trading activity at a particular price point is often indicative of a support level. This is because more traders are expressing interest in buying at this level.
However, not all traders use such a qualitative approach for identifying support levels. These days, many traders utilize various software tools and algorithms to identify support levels more precisely. This quantitative approach allows for quicker, more effective identification of support levels, making all the difference in fast-paced trading markets.
Remember, support levels—like all aspects of technical analysis—are not foolproof. They provide educated guesses about future price movements based on past data. Therefore, traders should always couple the identification of support levels with rigorous risk management techniques to minimize potential losses.
How to Spot Support Levels on Charts
Unearthing support levels on a trading chart can seem complex at first glance. It requires both understanding of the basic concepts and keen observation skills. Fortunately, there are several steps one can follow to simplify this task.
Step 1: Understand the Concept of Support Levels
At its core, support is the price level where a stock or commodity is expected to stop falling due to increased demand or buying interest. In theory, when the price falls towards a support level, it’s as if it’s falling into a safety net. Traders expect the support level to halt the downtrend, causing the price to stabilize or even rebound.
Step 2: Analyze Historical Prices
One effective way to identify support levels is by looking at a security’s past price levels that halted previous downtrends. Mapping out these distinct price points across the chart will give a trader insight into potential future support levels. This is based on the market psychology concept that what has occurred before is likely to occur again.
Step 3: Look for Consolidation Areas
Consolidation areas – periods where the price remains relatively stable for a while – are also indications of potential support levels. The longer the price stays within a specified range, the stronger the support level is considered to be. These areas can be visible in the form of rectangular patterns on charts.
Step4: Use Trend Lines
Trend lines are another crucial tool traders use to identify support levels. Drawn under the lows of the price during an uptrend, these lines show the level at which buying has consistently picked up during a specific period thus indicating a support level.
Step 5: Validate with Volume
Finally, traders tend to confirm the validity of a support level by checking for an increase in volume at or near that price. The logic behind this is that higher trading volumes indicate higher interest, which can be indicative of stronger support.
By following these steps systematically, a trader can successfully recognize support levels. Not only does this improve decision-making, but it also has a positive impact on trading outcomes.
Using Indicators to Confirm Support Levels
In the realm of technical analysis, indicators play a pivotal role in confirming support levels, enhancing traders’ ability to make more informed decisions. These tools offer additional confirmation signals, providing deeper insights into price movements and comprehension of the market’s overall momentum and direction.
Volume Indicators
Volume indicators are perhaps the most commonly used tools to confirm support levels. Essentially, these metrics provide information about the number of shares or contracts traded over a specified period. If a stock reaches a purported support level with heightened volume, there’s a strong likelihood that this level is valid. The reason lies in the market sentiment; larger volumes denote greater interest from traders, effectively supporting the price from falling below this level.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is another crucial tool commonly used to confirm support levels. The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. An RSI reading of 30 or below usually indicates that a security may be oversold, signaling a potential support level. Combining this information with other analytical techniques can augment the support level’s validity.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is an oscillating indicator that stipulates the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. Savvy traders will observe how the MACD interacts with support levels. When the MACD line crosses the signal line upward at a support level, this could clarify and confirm the identified support level.
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are volatility indicators that often prove beneficial in confirming support levels. They consist of a simple moving average (middle band) plus and minus one standard deviation (upper and lower band). The lower band often acts as a dynamic support level. If prices recoil upward after touching the lower band, it can reaffirm the support level.
In conclusion, integrating these indicators into one’s trading strategy can help identify and confirm valid support levels. Nonetheless, traders need to understand that no single indicator is infallible — employing a variety of these tools and combining them with other analytical techniques can lead to more robust and reliable trading strategies.
Strategies for Trading Support Levels
When it comes to trading, understanding how to work with support levels can be a significant asset. These levels provide a basis for creating effective and strategic trading decisions. Here are some renowned strategies for trading on these crucial price levels.
Buy Low, Sell High
The simple principle of ‘buy low, sell high’ stands as a foundational strategy for trading on support levels. When the price drops and approaches a support level, it presents traders with an opportunity to enter the market at a lower cost (buy low) and then sell when the price rebounds back up (sell high).
Bounce and Break Strategy
The ‘bounce and break’ strategy is centered around the concept of price behavior as it interacts with support levels. As the name suggests, there are two primary scenarios – a bounce where the price rebounds from the support level, and a break where the price falls through the support level. Traders aiming to apply the ‘bounce’ strategy would buy at the support level and sell at resistance, while those using the ‘break’ strategy would wait for the price to fall below support before selling.
Use of Stop-Loss Orders
Placing ‘stop-loss’ orders is an effective method used by traders to control risk when trading on support levels. A stop-loss order is designed to limit a trader’s loss on a trade by exiting the position if the price falls below a specific point, which is often placed just below the identified support level.
Support Becomes Resistance Strategy
In some instances, a broken support level can transform into a resistance level, and vice versa. This strategy, often known as the principle of ‘support becomes resistance’, allows traders to make trading decisions based on previous trends. If a price breaks through a support level, the trader may enter a short position with the expectation that the old support level will turn into a new resistance level.
Remember, no strategy is fool-proof, and these methods should be used in conjunction with other technical indicators and market factors. As with all trading strategies, maintaining discipline and employing effective risk management techniques are paramount to success.
Identifying Resistance Levels in Trading
Resistance levels in trading are critical points on a price chart that indicate a potential reversal of a price increase, acting as a ceiling that the asset’s price struggles to break through. Traders and investors utilize resistance levels to formulate crucial trading decisions, encompassing entry and exit points and stop-loss orders.
Identifying these resistance levels can substantially aid in mitigating potential losses and increasing profit potential. The process involves a blend of technical analysis, intuition, and past data to predict where these levels may develop.
Understand the Concept of Resistance Levels
Primarily, it’s vital to understand that resistance levels signify a price point where the selling interest surpasses buying interest. This surge in selling activity often results in the price’s inability to rise beyond this level, leading to a temporary or permanent reversal in the upward trend.
Utilize Past Data and Price History
An essential part in identifying resistance levels is analyzing historical price data. By studying where prices have failed to climb in the past, it becomes possible to identify potential resistance levels. These are the price levels where significant selling took place due to market participants’ collective belief that the asset was overpriced.
Observe Price Patterns and Consolidation Phases
Additionally, traders can spot resistance levels during consolidation phases, where the asset’s price movements are relatively small, signifying indecision in the market. These areas often occur before significant price jumps, either upward or downward. If the price moves downward after consolidation, the upper level of consolidation becomes a new potential resistance level.
Construct Trend Lines
Another method is to construct a trend line by connecting two or more high points on a price chart. A downward-sloping trend line created by connecting descending peaks can be regarded as a dynamic resistance level. The price encounters resistance and tends to fall each time it approaches this line.
Validation with Volume
Lastly, traders should validate potential resistance levels by observing trading volume. A resistance level is more valid if the price reversal occurs with a high volume. This reflects strong selling pressure and confirms that the price may struggle to break above this level in the future.
How to Spot Resistance Levels on Charts
Spotting resistance levels on a chart can be a beneficial skill for any trader. Often, resistance levels represent psychological price points at which sellers gain enough control to inhibit buyers. By identifying these points, traders can anticipate potential price reversals and adjust their strategies accordingly. Here’s how to do it:
1. Understand Price Patterns
The journey to spotting resistance levels starts with understanding the structure of price charts. The most common price patterns, such as double tops, triple tops, and head and shoulders patterns, all indicate potential resistance levels. When you notice these patterns forming, consider it a warning sign that resistance may be building.
2. Keep an Eye on Previous Highs
Looking at the historical data, particularly past highs, can provide a valuable insight into where resistance may form. The rationale behind this is simple – if buyers couldn’t surpass a certain level before, they may struggle to do it again. Include these levels in your analysis.
3. Draw Trend Lines
Plotting lines that join together the successive peaks on a chart can be an effective way to illustrate resistance levels. These trend lines, especially if they are tested multiple times, can offer solid reflections of the selling pressure experienced at these points.
4. Use Intraday Resistance Levels
In intraday trading, resistance can often be seen in the Pivot Point levels. These are widely-used indicators that divide the previous day’s high, low, and closing price by three to give a set of price levels that might act as support or resistance. Recognize that the levels R1, R2, and R3 are potential resistance zones.
5. Overlay Technical Indicators
Finally, using technical indicators can help confirm or disprove suspected resistance levels. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD) are often used to identify overbought conditions that indicate resistance. If these indicators show a market is overbought when it reaches a suspected resistance level, it strengthens the case that such level is indeed a valid resistance.
By considering these steps, traders can enhance their ability to spot resistance levels, and make informed decisions based on a thorough analysis of chart data.
Key Characteristics of Resistance Levels
Resistance levels play a crucial role in technical analysis and serve as a decisive factor for traders in both short-term and long-term market scenarios. Knowing the key characteristics of resistance levels can significantly increase the efficiency and accuracy of strategic decision-making. Below are the main attributes that define these levels:
1. Reversal Point
A resistance level is often perceived as a price ceiling at which the asset’s price tends to halt and reverse its upward trajectory. As a significant selling pressure area, this level indicates where the supply (selling activity) exceeds the demand (buying interest), causing a price drop.
2. An Area of Struggle
Existing at the point where sellers outnumber buyers, resistance levels mark a battleground between bulls (buyers) and bears (sellers). This tussle is visible through price patterns such as consolidation or increased volatility near this level.
3. Psychological Barrier
Resistance levels often represent psychological barriers in the market, where participants tend to sell their holdings due to fear of the asset price not rising further. These round or attractive numbers are crucial to traders and investors, as they may behave erratically around these points, providing unique trading opportunities.
4. Multiple Touch Points
Strong resistance levels are usually validated by multiple touch points. The more times the price touches this level and reverses, the stronger the resistance is considered. Once the price breaks through, it could signify a new upward trend, though a confirmation is needed to validate this shift.
5. Volume Amplification
High trading volume is another feature of resistance levels. An increase in volume often comes from increased selling activity as the asset price nears the resistance level. By observing the volume, traders can gauge the strength of the resistance and the reliability of a potential breakout.
6. Role Reversal
Following a breakout, resistance levels can transform into support levels. This phenomenon, known as the ‘role reversal,’ implies that traders who once sold their assets due to fear of price drop now start buying at this level, expecting it to serve as a new floor for future price actions.
By understanding these characteristics, traders can better interpret market trends and direct their trading strategies accordingly.
Strategies for Trading Resistance Levels
The trading of resistance levels can be a critical aspect of a trader’s strategy. There are a variety of methods used by professionals to take advantage of these levels in their trading plan. Below we explore several prominent strategies including the use of trend line breaks, monitoring for failure swings, implementing the concept of throwback and utilizing the principle of resistance becoming support.
Trend Line Breaks
A commonly used strategy involves trading trend line breaks. A resistance level breakout is usually accompanied by a significant increase in volume, indicating that the price has the momentum to move higher. Traders might consider entering a long position when this occurs, anticipating further price rises.
Monitoring for Failure Swings
A failure swing is an instance where the price tries to break past the resistance level but is unsuccessful, ultimately creating a swing high. This is often a bearish sign that the price might soon decrease, which can provide a selling opportunity for traders. By identifying failure swings, a trader can potentially position themselves to take advantage of upcoming price movements.
Throwback
The concept of throwback refers to a situation where price breaks through resistance and then returns to that level before bouncing off it and continuing its upward move. The moment of return back to the broken level of resistance, which can now be considered a new level of support, might be an advantageous entry point for a long position.
Resistance Becomes Support
Often, once a resistance level has been broken, it can turn into a new support level. This is known as the principle of resistance becoming support. Traders can use this strategy to enter a trade at the new support level, anticipating that the price will bounce back and move upwards again.
In conclusion, trading resistance levels requires deep technical analysis and understanding of market psychology. It comes with its set of risks and, as with all aspects of trading, it’s crucial to employ careful risk management strategies such as setting stop-loss orders. Furthermore, these strategies should always be used in conjunction with other technical indicators and methods, ensuring a more comprehensive understanding of market movements.
Conclusion: Mastering Support and Resistance for Successful Trading
Mastering the concepts of support and resistance is instrumental to successful trading, especially in volatile markets. They mark crucial thresholds on charts where price actions can change rapidly, offering traders important insight to time their trades efficiently and effectively.
Support and resistance levels portray the tug of war between bulls (buyers) and bears (sellers) in the market. Understanding the mechanics behind their formation enhances a trader’s knowledge about how supply and demand shapes markets. By successfully identifying these levels, a trader can anticipate potential price reversals and implement appropriate trading strategies accordingly.
Utilizing both historical data and technical indicators is critical in assessing these levels. Indicators such as the Volume Indicators, Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Bollinger Bands can aid traders to confirm, validate, and anticipate these levels.
Moreover, deploying various trade strategies on these levels such as “Buy Low, Sell High”, “Bounce and Break Strategy”, and usage of “Stop-Loss Orders” can greatly enhance a trader’s potential for profitability. Being able to switch perspectives when support levels become resistance levels, and vice versa, can provide an edge in identifying subsequent opportunities.
In conclusion, trading without understanding support and resistance is akin to navigating a ship without a compass. The realms of support and resistance offer vital information about market trends, potential reversal points, and areas of price stabilization. Applying this knowledge effectively can pave the way for successful trading undertakings.
As with any strategy and information in trading, it’s vital to remember that while support and resistance levels provide valuable guidance, they are not foolproof. Implementing good risk management practices, along with a disciplined trading plan, is indispensable in the path to becoming a prosperous and sustained trader.