Types of Cyber Attacks That Cost US Businesses $10.5 Trillion This Year

My phone rang at 2:47 AM last Tuesday. That’s never good news in cybersecurity. “They got us,” the voice said. It was the CISO of a Fortune 500 company, and he sounded like he’d aged ten years since our last golf game. “Ransomware. Everything east of Chicago is locked. They want fifty million.” Fifty. Million. Dollars.
This company has a security budget that would make your eyes water. Top-tier firewalls, 24/7 SOC, the works. Didn’t matter. The attackers found the one legacy system everyone forgot about – an old HR portal that “wasn’t worth updating.” Guess it’s worth fifty million now.
The thing is, this isn’t unusual anymore. According to the FBI’s 2024 Internet Crime Report, US businesses reported losses exceeding $16.6 billion from cyber attacks – a 33% increase from 2023. And that’s just what gets reported. Industry estimates put the real damage at $10.5 trillion when you factor in unreported incidents, downtime, and reputation damage. I had to read it three times myself. When I started in this field, a million-dollar breach made headlines. Now? That’s a slow Tuesday.
You know what really gets me though? After fifteen years of cleaning up these disasters, the pattern’s always the same. Companies obsess over one threat – usually whatever made the news last – while leaving barn doors wide open everywhere else. They’ll spend millions preventing the last war while tomorrow’s attack walks right through the front door.
So here’s what we’re doing. I’m walking you through every major type of cyber attack that’s actively hunting US businesses right now. Not the theoretical stuff from security conferences – the real attacks that are destroying companies as you read this. Some of it’s going to sound paranoid. Good. In this business, paranoia is just another word for experience.
Fair warning: this is comprehensive. If you want quick fixes or magic bullets, you’re in the wrong place. But if you’re serious about understanding the different types of cyber attacks that could end your career or your company, pour yourself something strong and keep reading. I’ve linked out to our deep-dive guides on each attack type for when you need the full technical breakdown.
Ready? Let’s talk about why your infrastructure is probably already compromised.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Current Cyber Threat Landscape
The numbers are sobering. According to CISA’s latest threat assessment, US businesses face an average of 2,200 cyber attacks per day. And that’s just the ones we know about. The reality? Most companies don’t even realize they’ve been breached until it’s too late.
What’s changed in 2025? Everything. The common cyber attack methods have evolved from simple phishing emails to sophisticated AI-powered campaigns that can mimic your CEO’s writing style perfectly. State-sponsored groups from Russia, China, and North Korea are targeting everything from small manufacturers in Ohio to tech giants in Silicon Valley.
Here’s what’s hitting American businesses hardest right now:
- Ransomware attacks have increased 150% since 2024, with average ransom demands reaching $5.3 million
- Supply chain attacks are targeting the weakest link – that small vendor you forgot about
- AI-enhanced phishing that’s so convincing, even security professionals are getting fooled
- Cloud infrastructure attacks exploiting the rush to remote work
- Zero-day exploits being weaponized within hours of discovery
CISA’s latest threat assessments track over 2,200 cyber attacks hitting US infrastructure daily. And that’s just the ones we know about. The reality? Most companies don’t even realize they’ve been breached until it’s too late.
But here’s the thing – and this is why I’m writing this guide – most of these attacks are preventable. Not with some magic security tool (despite what vendors tell you), but with understanding. You need to know what types of cyber attacks exist, how they work, and where your vulnerabilities lie.
Over the next sections, we’ll explore each category of attack in detail. I’ll show you what to watch for, share some war stories from the trenches, and point you to our specialized guides for deeper dives. Because in cybersecurity, knowledge isn’t just power – it’s survival.
Network-Based Cyber Attacks Every IT Professional Should Know
Network security attacks are like termites – by the time you see the damage, the structure is already compromised. I learned this the hard way when a client’s entire West Coast operation went dark during Black Friday. Turned out, attackers had been living in their network for three months.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Remember when DDoS attacks were just script kiddies showing off? Those days are long gone. Modern DDoS attacks are surgical strikes designed to cripple specific services at the worst possible moment. Last month, a major e-commerce platform lost $12 million in 6 hours when attackers hit during their flash sale.
The scary part? DDoS-for-hire services now cost less than your monthly Netflix subscription. Any disgruntled competitor can launch an attack that would have required nation-state resources just five years ago. When DDoS attacks hit your infrastructure, here’s what you need to know.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
MITM attacks are the digital equivalent of someone reading your mail before it reaches your mailbox. Except instead of birthday cards, we’re talking about credit card numbers, login credentials, and sensitive business communications.
What drives me crazy about MITM attacks is how preventable they are. Yet I still see companies transmitting sensitive data over unencrypted connections. Just last week, I found a healthcare provider sending patient records through plain HTTP. In 2025! Network security requires understanding man-in-the-middle attack vectors at a technical level.
Network Sniffing and Packet Capture
Here’s an uncomfortable truth: if attackers get into your network, they can see everything. Network sniffers capture data packets flying across your infrastructure like a surveillance camera for your digital traffic. The types of cyber attacks using packet capture have become incredibly sophisticated – attackers aren’t just grabbing passwords anymore. They’re mapping your entire network topology, identifying key systems, and planning their next move.
DNS Hijacking and Cache Poisoning
Ever typed in your bank’s website and ended up somewhere else? That’s DNS hijacking in action. Attackers redirect your traffic to malicious servers that look exactly like the real thing. The number of different types of cyber attacks targeting DNS infrastructure has exploded because it’s such an effective vector.
And here’s what really bothers me – most organizations treat DNS like plumbing. Set it and forget it. Big mistake. DNS is the foundation of your network. When it’s compromised, everything built on top crumbles.
Malware and Software-Based Attack Types
Let me tell you about the moment I realized malware had evolved beyond our defenses. It was 3 AM, and I was staring at a ransomware note on a client’s screen. The malware had encrypted 10 years of research data. The kicker? Their antivirus had given it a clean bill of health just hours before.
The Ransomware Epidemic
Ransomware isn’t just locking files anymore – it’s a full-scale business model. Modern ransomware groups operate like Fortune 500 companies, complete with customer service (I’m not kidding) and affiliate programs. They research their targets, know exactly how much you can afford to pay, and time their attacks for maximum impact.
The different types of cyber attacks in the malware family have exploded in sophistication. We’re seeing:
- Double extortion: Encrypt your data AND threaten to leak it
- Triple extortion: Add DDoS attacks to the mix if you don’t pay
- Supply chain ransomware: Hit your vendors to get to you
We dive deep into malware protection strategies in our comprehensive malware guide, but here’s the bottom line: if you’re still relying on signature-based antivirus in 2025, you’re bringing a knife to a gunfight.
Trojans: The Digital Trojan Horse
The name hasn’t changed since ancient Greece, but modern trojans are nothing like their ancestors. Today’s trojans are modular, updatable, and incredibly stealthy. They masquerade as legitimate software – that PDF reader update, that browser extension for productivity – while opening backdoors into your system.
What’s particularly nasty about current trojans is their patience. They’ll sit dormant for months, learning your network, stealing credentials, and waiting for the perfect moment to strike. I’ve seen trojans that only activate when they detect a certain bank’s website, or when specific files are accessed.
Spyware and Information Stealers
Here’s something that’ll make you paranoid: modern spyware can turn every device in your organization into a surveillance tool. Webcams, microphones, keystrokes – everything becomes a data source for attackers. And it’s not just state-sponsored groups anymore. Corporate espionage using commercial spyware is rampant.
The types of cyber attacks using spyware have become incredibly targeted. Attackers aren’t casting wide nets – they’re spear-fishing for specific executives, engineers with trade secrets, or employees with financial access.
Supply Chain Attacks: The New Frontier
Remember SolarWinds? That was just the beginning. Supply chain attacks are the nuclear weapons of cybersecurity – one compromised vendor can take down thousands of companies. And here’s the terrifying part: you can do everything right and still get hit because someone else didn’t.
These common cyber attack methods work because we trust our vendors. That software update from your accounting platform? That plugin for your development environment? Each one is a potential trojan horse. The types of cyber attacks targeting supply chains have made “trust but verify” obsolete. Now it’s “never trust, always verify.”

Social Engineering and Human-Focused Attack Methods
You know what’s funny? (Well, not really funny – more like tragically ironic.) Companies spend millions on firewalls and encryption, then Karen from accounting wires $50,000 to a fake vendor because the email “seemed urgent.” Human beings remain the weakest link in cybersecurity, and attackers know it.
Phishing: Still the King of Cyber Attacks
I’ll be honest – phishing attacks in 2025 make me genuinely angry. Not because they’re sophisticated (though they are), but because they’re so damn effective. AI has transformed phishing from spray-and-pray to surgical precision. Attackers scrape LinkedIn, analyze writing patterns, and craft emails that would fool anyone.
Last month, I tested a client’s employees with a phishing simulation. The email appeared to come from their CEO, used his writing style, referenced a real project, and asked for “quick feedback” on a document. 73% clicked the link. Seventy. Three. Percent.
The different types of cyber attacks using phishing as an entry point are staggering:
- Spear phishing: Targeted attacks on specific individuals
- Whaling: Going after the C-suite big fish
- Vishing: Voice phishing over phone calls
- Smishing: SMS-based phishing (yes, that’s a real term)
For step-by-step phishing prevention, check out our practical prevention guide. But here’s my quick tip: if an email makes you feel rushed, stressed, or excited – stop. That emotional response is exactly what attackers are counting on.
Social Engineering: Hacking Humans
Social engineering is psychological warfare, plain and simple. And the types of cyber attacks using social engineering are limited only by human creativity and malice. These aren’t just “confidence tricks” anymore – they’re orchestrated psychological operations.
I once watched (ethically, during a penetration test) as an attacker called a company’s IT help desk. He knew the name of an employee on vacation, claimed to be them, said he was locked out of his account while traveling for an urgent client meeting. Even threw in some background office noise and complained about the hotel wifi. Got full VPN credentials in under 5 minutes.
Understanding the psychology behind these attacks? Our social engineering analysis breaks it down. But here’s what you need to know now: social engineers exploit trust, authority, urgency, and fear. They’ve studied human psychology better than most therapists.
Insider Threats: The Enemy Within
This is the attack type that keeps me up at night. Not because insider threats are common (though they’re more frequent than you’d think), but because they’re so hard to detect and devastating when they hit. Whether it’s a disgruntled employee, a compromised account, or someone who just made a stupid mistake – insider threats bypass most traditional security measures.
The types of cyber attacks from insiders range from:
- Intentional data theft (selling trade secrets)
- Sabotage (deleting critical data before quitting)
- Accidental exposure (misconfigured cloud storage)
- Compromised insiders (employees whose accounts are hijacked)
Internal threats deserve special attention – our insider threat guide explains why. But here’s my take: most insider threats aren’t malicious. They’re mistakes. And you prevent mistakes through training, clear policies, and systems that make it hard to do the wrong thing.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
BEC is the white-collar crime of the digital age. Attackers impersonate executives, vendors, or partners to trick employees into transferring money or sensitive data. And business is booming – the FBI reports BEC losses exceeded $2.4 billion last year in the US alone.
What makes BEC particularly nasty is that it often doesn’t involve malware or technical exploits. It’s pure social engineering. Attackers study your organization, learn who has financial authority, understand your procedures, then strike when key people are traveling or distracted.

Web Application and Database Attack Vectors
Here’s something that’ll make your blood run cold: 83% of web applications have at least one serious security vulnerability. I’m not making that up – that’s from the latest OWASP report. And developers, bless their hearts, keep making the same mistakes that enable these common cyber attack methods.
SQL Injection: The Zombie That Won’t Die
SQL injection should be dead. We’ve known how to prevent it for two decades. Yet here I am in 2025, still finding SQL injection vulnerabilities in production applications. Just last quarter, a major retail chain lost 4 million customer records to a SQL injection attack that would have been prevented by basic input validation.
The types of cyber attacks using SQL injection have evolved, but the core problem remains: applications trusting user input. Modern attackers use automated tools to find and exploit these vulnerabilities at scale. They’re not manually typing SQL commands anymore – they’re running sophisticated scanners that can compromise hundreds of sites per hour.
Developers especially need our detailed SQL injection prevention guide. But here’s the TLDR: parameterized queries, input validation, and least-privilege database accounts. It’s not rocket science, but it requires discipline.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): JavaScript Gone Rogue
XSS attacks turn your own website against your users. Attackers inject malicious JavaScript that executes in victims’ browsers, stealing session cookies, capturing keystrokes, or redirecting to phishing sites. And with modern web applications being basically JavaScript delivery platforms, the attack surface is massive.
What’s particularly frustrating about XSS is how subtle it can be. That comment form on your blog? That search box? That user profile field? Each one is a potential injection point. And the different types of cyber attacks using XSS are limited only by JavaScript’s capabilities – which is to say, nearly limitless.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): The Confused Deputy
CSRF tricks your browser into making requests you didn’t intend. Imagine clicking a link in an email and unknowingly transferring money from your bank account. That’s CSRF in action. Your browser, trying to be helpful by including authentication cookies, becomes an unwitting accomplice.
These network security attacks are particularly insidious because they abuse the trust between users and websites. The types of cyber attacks leveraging CSRF often go unnoticed until the damage is done – money transferred, settings changed, data deleted.
API Security: The New Battleground
APIs are the glue holding modern applications together. They’re also a massive security hole. Every API endpoint is a potential attack vector, and most organizations have no idea how many APIs they’re actually running. I recently audited a client who thought they had 50 APIs. We found 400.
The cyber security threats targeting APIs include:
- Authentication bypass
- Rate limiting abuse
- Data exposure through verbose errors
- Injection attacks through JSON payloads
- Business logic flaws
APIs power everything from mobile apps to IoT devices, making them incredibly attractive targets. The types of cyber attacks against APIs are evolving rapidly as attackers realize many organizations haven’t caught up to API security best practices.
Advanced and Emerging Cyber Attack Types
Buckle up, because this is where things get scary. The types of cyber attacks I’m about to describe aren’t your garden-variety threats. These are the operations that make seasoned security professionals lose sleep.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): The Long Game
APTs are like having an invisible spy living in your house for months, documenting everything, waiting for the perfect moment to strike. These aren’t smash-and-grab operations – they’re patient, methodical, and devastatingly effective.
I once worked an incident where attackers had been in the network for 18 months. Eighteen months! They moved slowly, carefully, learning the environment better than the IT team. By the time they activated, they had admin access to everything. The different types of cyber attacks within the APT category share this patience and sophistication.
Nation-states are the usual suspects – China’s APT groups targeting intellectual property, Russia’s crews hitting critical infrastructure, North Korea funding their regime through cybercrime. But increasingly, criminal groups are adopting APT tactics. Enterprise teams should understand advanced persistent threat tactics because when you’re targeted by an APT, it’s not if they’ll get in – it’s when.
Zero-Day Exploits: Unknown Unknowns
Zero-days are the bogeymen of cybersecurity – vulnerabilities nobody knows about except the attackers. By definition, there’s no patch, no signature, no defense except good security architecture and a bit of luck.
The zero-day market is booming. A good iOS zero-day can sell for $2 million on the black market. Windows zero-days go for six figures. And here’s the kicker – the types of cyber attacks using zero-days aren’t always from criminals. Governments stockpile them, security companies hoard them, and sometimes employees sell them to the highest bidder.
AI-Powered Attacks: The Rise of the Machines
If you think AI is just for chatbots and image generation, I’ve got bad news. Attackers are using AI to supercharge every type of cyber attack in their arsenal. AI writes phishing emails that pass every linguistic test. It generates deepfake audio for vishing attacks. It finds vulnerabilities faster than human researchers.
But here’s what really concerns me: AI attacks that learn and adapt in real-time. Imagine malware that rewrites itself to evade detection, or attacks that analyze your defense patterns and adjust tactics accordingly. We’re not quite there yet, but we’re close. Terrifyingly close.
IoT and Cloud-Specific Threats
The rush to cloud and IoT has created a security nightmare. Every smart device is a potential entry point. Every misconfigured S3 bucket is a data breach waiting to happen. The types of cyber attacks targeting cloud infrastructure have exploded because, frankly, most organizations don’t understand the shared responsibility model.
I can’t tell you how many times I’ve heard “But AWS/Azure/Google handles security!” No, they secure the infrastructure. You secure what you put on it. That misconfigured database exposing millions of records? That’s on you. Cloud environments face unique challenges covered in our cloud security guide.
The cyber threat landscape now includes:
- Cryptojacking in cloud environments
- IoT botnets larger than some countries’ populations
- Serverless function abuse
- Container escape attacks
- Multi-cloud attack chains
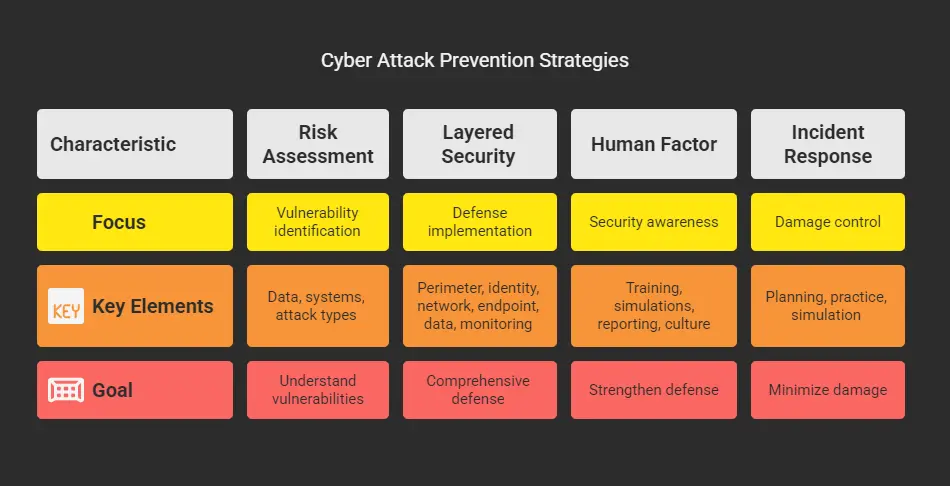
Building Your Cyber Attack Prevention Strategy
Alright, deep breath. I know I’ve just spent several thousand words scaring the hell out of you. But here’s the thing – understanding these types of cyber attacks is the first step to defending against them. And defense is absolutely possible.
Risk Assessment: Know Your Battlefield
You can’t defend everything equally. Trust me, I’ve watched organizations try, and they end up defending nothing well. Start with a honest assessment: What data would hurt most if stolen? What systems would cripple operations if offline? What types of cyber attacks are most likely given your industry?
A proper risk assessment isn’t a checkbox exercise. It’s a brutal examination of your vulnerabilities. And here’s my unpopular opinion: most organizations need outside eyes for this. You’re too close to your own environment to see all the gaps.
The Layered Security Approach
Security isn’t a product – it’s a process. (I know, I know, that sounds like consultant-speak, but stick with me.) The most effective defense against different types of cyber attacks is layers. Think of it like a medieval castle:
- Perimeter defenses (firewalls, IDS/IPS)
- Identity and access management (who gets in)
- Network segmentation (limit lateral movement)
- Endpoint protection (every device is a battlefield)
- Data protection (encryption, DLP)
- Monitoring and response (see everything, respond fast)
Building comprehensive defense? Start with our zero trust implementation strategy. Zero trust isn’t just another buzzword – it’s a fundamental shift in how we think about security. Trust nothing, verify everything.
The Human Factor: Your Weakest Link or Strongest Defense
I’ve seen million-dollar security programs fail because nobody trained the receptionist. Your people are either your biggest vulnerability or your best defense – the choice is yours. And I mean real training, not those awful annual videos everyone clicks through while checking email.
Effective security awareness means:
- Regular, engaging training on current threats
- Simulated attacks (with learning, not punishment)
- Clear reporting procedures
- A culture where security is everyone’s job
The types of cyber attacks targeting humans aren’t going away. If anything, they’re getting more sophisticated. But humans can also be incredibly good at detecting something “off” – if they know what to look for.
Incident Response: When (Not If) You Get Hit
Let’s be real – with all these types of cyber attacks out there, eventually something will get through. The difference between a minor incident and a catastrophe is preparation. Yet most incident response plans are fantasy documents that fall apart at first contact with reality.
When attacks succeed, our incident response planning guide becomes critical. But here’s my advice: practice. Run tabletop exercises. Simulate breaches. Break things in controlled ways. Because finding out your backup restore process doesn’t work during a real ransomware attack? That’s a career-ending discovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common types of cyber attacks in 2025?
The most common types of cyber attacks hitting US businesses right now are ransomware (affecting 37% of organizations), phishing attacks (responsible for 91% of breaches), and business email compromise (causing $2.4 billion in losses). DDoS attacks and supply chain compromises round out the top five. What’s changed is the sophistication – these aren’t your 2020-era attacks anymore.
How do different types of cyber attacks affect small vs enterprise businesses?
Here’s the brutal truth: small businesses often get hit harder despite being targeted less. Enterprises face more advanced persistent threats and zero-day exploits, but they have resources to recover. Small businesses? One ransomware attack demanding $50,000 might mean closing doors. The types of cyber attacks vary, but small businesses see more opportunistic attacks (automated scans, spray-and-pray phishing) while enterprises face targeted operations. Both need protection, just different strategies.
Which cyber attack types are most dangerous for US companies?
Hands down, supply chain attacks and ransomware are the most dangerous types of cyber attacks for US companies right now. Supply chain attacks like SolarWinds can compromise thousands of organizations through a single vendor. Ransomware doesn’t just encrypt data anymore – attackers steal it first, then threaten to leak it. Combined with the average 23-day downtime, it’s devastating. APTs are scarier but less common unless you’re in defense, tech, or critical infrastructure.
How often should organizations assess different cyber attack types?
If you’re assessing annually, you’re already behind. The threat landscape changes monthly. I recommend quarterly deep-dives on the types of cyber attacks relevant to your industry, with monthly threat intelligence briefs. After any major incident in your sector, do an immediate assessment. And here’s the key – assessments aren’t just about new threats. They’re about checking if your defenses against known attack types are still working.
What’s the average cost of different types of cyber attacks?
Brace yourself: IBM’s latest report puts the average data breach at $4.88 million for US companies. But that’s an average. Ransomware attacks average $5.13 million when you factor in downtime, recovery, and often paying the ransom (yes, despite FBI recommendations). Insider threats? $15.38 million on average because they take 85 days longer to detect. BEC attacks average “only” $125,000 per incident, but they happen constantly. The real cost of any cyber attack includes customers lost, reputation damage, and sleepless nights – things you can’t put a price on.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead in the Cyber Arms Race
Look, I’ve thrown a lot at you in this guide. The types of cyber attacks threatening US businesses in 2025 are numerous, sophisticated, and evolving constantly. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, that’s normal. Hell, I’ve been doing this for over a decade and I still learn about new attack vectors weekly.
But here’s what I want you to remember: perfect security is impossible, but good security is achievable. Every defense you implement, every employee you train, every vulnerability you patch – it all makes you a harder target. And in cybersecurity, you don’t have to outrun the bear. You just have to outrun the other guy.
The cyber threat landscape will continue evolving. AI will make attacks more sophisticated. Quantum computing will break current encryption. New technologies will create new vulnerabilities. But the fundamentals remain: understand your threats, layer your defenses, train your people, and prepare for incidents.
Start with our detailed prevention guides below. Pick the types of cyber attacks most relevant to your organization and dive deep. Build your defenses methodically. And remember – in the war against cyber attacks, knowledge is your best weapon.
Stay safe out there. And seriously, patch your systems.